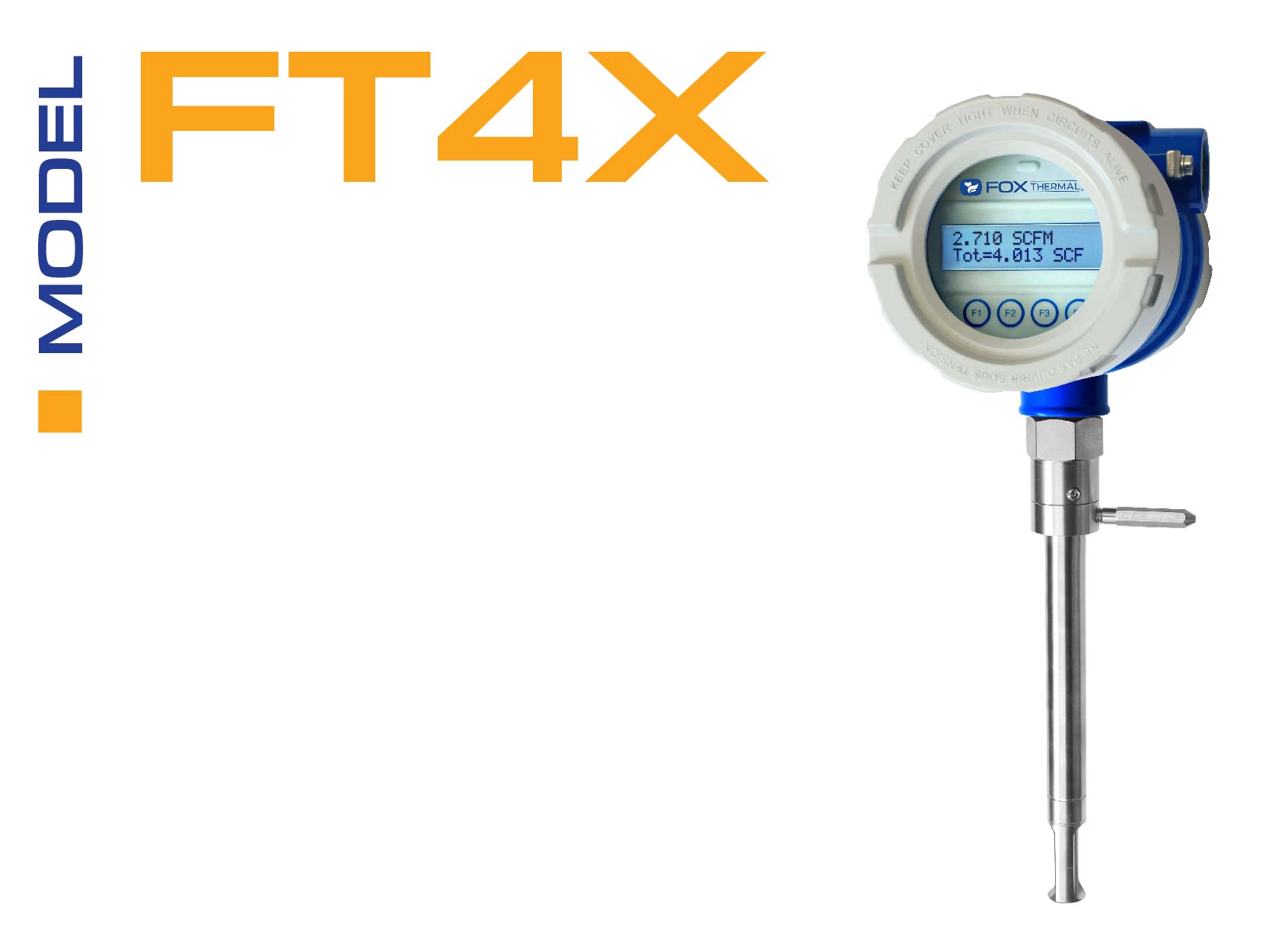
Natural Gas Flow Meter FAQs
How are flow meters used for sub-metering utility natural gas feed?
Natural gas flow meters are extensively used for sub-metering utility natural gas feeds to identify usage and potential leaks across different buildings or processes. This practice allows industrial facilities to monitor and manage their natural gas consumption more effectively, helping to detect abnormalities and inefficiencies. For example, a large manufacturing plant might install flow meters at various points in its gas distribution system to track consumption in different departments. By analyzing the data, the facility can identify areas with unusual gas usage patterns, which might indicate leaks or opportunities for energy-saving measures.
Are natural gas flow meters commonly used to help optimize combustion equipment?
Another common application of natural gas flow meters is monitoring the gas feed to burners in combustion equipment. These meters play a critical role in optimizing the air-to-fuel ratio for better efficiency and reduced emissions. For instance, in a power plant, flow meters can be used to ensure that the right amount of natural gas is delivered to the boilers. By continuously adjusting the gas feed based on real-time measurements, the plant can achieve optimal combustion efficiency, leading to lower fuel costs and a significant reduction in harmful emissions.
How do I optimize furnaces, boilers, and ovens?
Using natural gas flow meters to optimize furnaces, boilers, and ovens helps ensure that the air-to-fuel ratio is maintained at an ideal level. This optimization leads to better combustion efficiency, resulting in reduced fuel costs and lower emissions. It also helps to maintain consistent temperatures, which is crucial for the quality of products being processed.
What is an effective strategy for improving the efficiency of heaters and kilns?
In heaters and kilns, natural gas flow meters can be used to regulate the gas feed precisely. This regulation ensures that these systems operate at peak efficiency, providing uniform heating and processing. Optimizing these pieces of equipment can lead to significant energy savings and improved product quality.
Can natural gas flow meters help optimize smelters and dryers?
For smelters and dryers, natural gas flow meters play a critical role in controlling the gas supply to maintain the necessary temperatures for efficient operation. Proper optimization helps in reducing energy consumption and minimizing operational costs. It also ensures that the end products meet stringent quality standards.
How do natural gas flow meters enhance heat-treating system performance?
Heat-treating systems benefit immensely from the precise control provided by natural gas flow meters. By optimizing the gas feed, these systems can achieve the exact temperatures required for specific treatments, ensuring the desired properties of the materials being treated. This leads to higher-quality products and reduced energy usage.
Can backup power systems be optimized using natural gas flow meters?
In backup power systems, natural gas flow meters help in monitoring and optimizing the fuel supply to generators. This optimization ensures that the generators operate efficiently during power outages, providing reliable backup power while conserving fuel and minimizing emissions.
How are natural gas flow meters used in emission reduction systems?
Natural gas flow meters are crucial in emission reduction systems like thermal oxidizers and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems, where precise control of the gas feed helps in reducing harmful emissions. By optimizing the gas feeds, these systems can operate more effectively, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and contributing to a cleaner environment.
How can natural gas flow meters help me track usage across multiple buildings or processes?
Natural gas flow meters can help you track usage across multiple buildings or processes by providing detailed monitoring of your natural gas consumption. By installing flow meters at various points in your gas distribution system, you can obtain precise data about the gas usage in different departments or buildings. This enables you to detect inefficiencies, identify potential leaks, and take corrective actions. For example, a manufacturing plant could use this information to pinpoint areas with high consumption and implement energy-saving measures, ensuring efficient and cost-effective operations.
What is the standard gas composition of "natural gas"?
The main component of natural gas is methane, although it often includes other gases in smaller quantities. "Pipeline quality" natural gas is defined as natural gas that meets specific standards for commercial use. It contains at least 90% methane by volume and must adhere to other criteria such as delivery pressure, delivery temperature, thermal content (BTU), and acceptable levels of trace gases and elements.
According to the North American Energy Standards Board (NAESB), the typical composition of natural gas includes methane (94.9%), ethane (2.5%), propane (0.2%), nitrogen (1.6%), carbon dioxide (0.7%), and trace gases (0.1%) such as iso-butane, normal butane, oxygen, iso-pentane, hexanes+, and hydrogen.
When ordering a flow meter, it's important to consult with the manufacturer regarding the gas composition settings they use for calibrating the meter for "natural gas." The factory settings might differ from your specific process needs, making it necessary to provide a gas composition analysis to ensure the calibration matches your process conditions.
When I choose "natural gas" from the Gas-SelectX® feature, what are the percentages of the gas constituents set?
The default composition of "Natural gas" in the Gas-SelectX® menu is based on the North American Energy Standards Board (NAESB) average for natural gas chemical composition. More specifically, what's programmed is 94.9% methane, 2.5% ethane, 0.3% propane, 1.6% nitrogen, and 0.7% carbon dioxide, but if your natural gas composition differs, the correct gas analysis percentages should be programmed into the gas mix menu. The menus are accessed from the meter's front display panel, software, or Modbus RS485.
What regulations impact the use of natural gas flow meters for industrial processes?
California Assembly Bill 32 (AB32) regulates and aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, with the Air Resources Board enforcing compliance. Accurate flow measurement devices are essential for facilities to monitor emissions, keep records, and meet AB32 reporting and reduction standards.
EPA's 40 CFR Part 98 requires specific facilities and suppliers to report greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions under the Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program (GHGRP). This helps monitor emissions, identify ways to reduce pollution, and cut costs. Natural gas flow meters assist operators in meeting these requirements.