Pressure Drop Defined
The pressure inside of a pipe can be different than the ambient pressure outside of the process. A pressure drop in the system can be caused by friction or a physical obstruction in the pipe that results in a loss of line pressure.
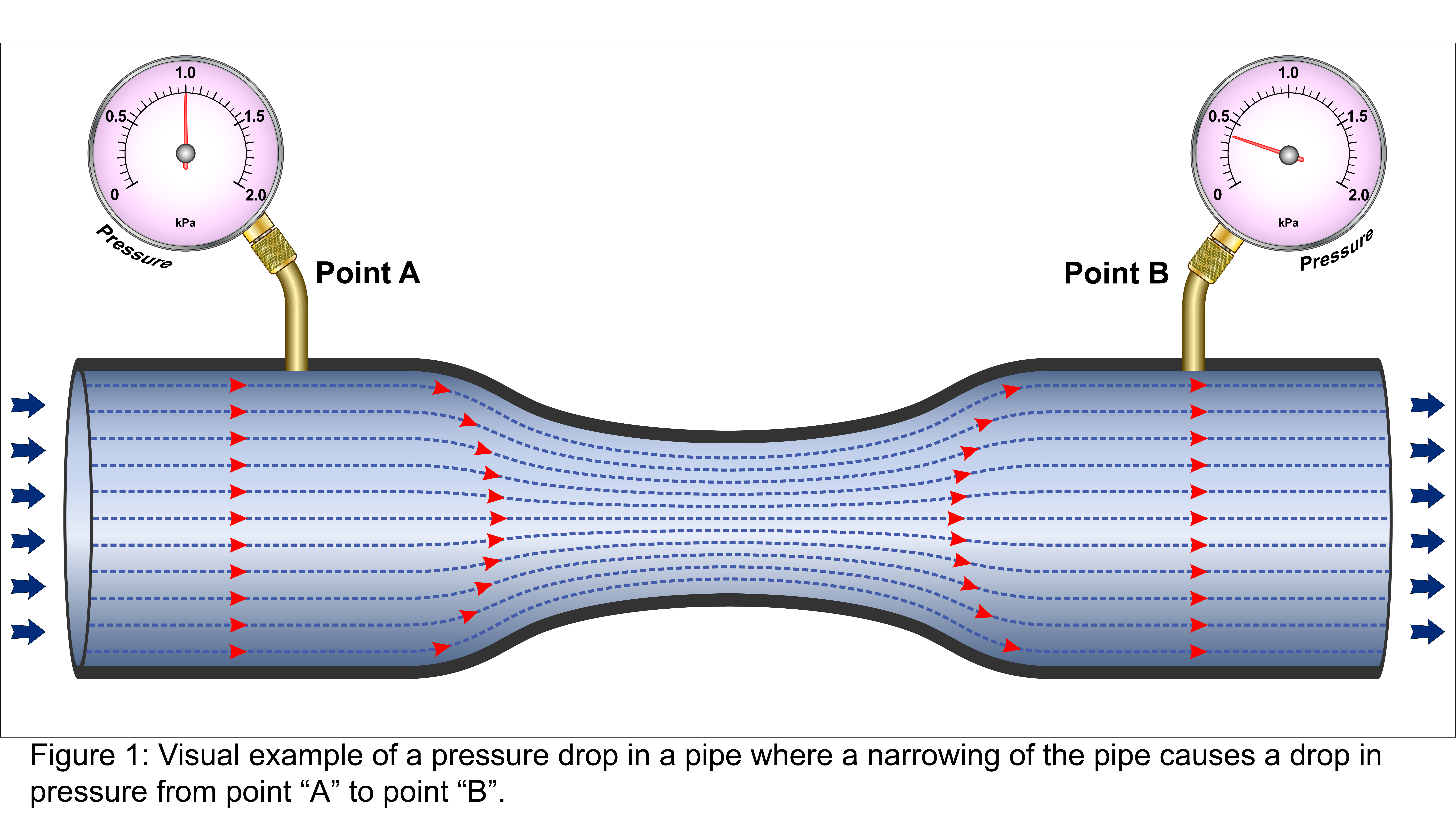
In Figure 1, we see a robust and high pressure reading at point “A” after which the pipe narrows. Then at point “B” we see a drop in the pressure reading. This is what is meant by pressure drop.
Maintaining pressure may have critical importance to the operation of the system, its equipment components, or the output of the process.
Typical causes of pressure drop:
- Friction from the walls of the pipe against the gas particles
- Bends in or narrowing of the pipe
- Obstructions inside of the pipe
- Sensors, probes, or other instruments inserted into the flow stream
- Leaks in the walls of the pipe
- Leaks from equipment installed on the pipe or in the process
Gas Flow Technologies and Pressure Drop Rates
There are many flow measurement technologies on the market today. Each technology uses different methods to arrive at a calculated flow rate in a pipe, but some technologies are known for causing pressure drops that may be undesirable. Once the pressure drops, it is unrecoverable. Let’s look at some common flow measurement technologies and their pressure drop ratings.

Negligible Pressure Drop in Thermal Mass Flow Meters
Thermal mass flow meters offer a direct mass flow measurement of air and gases in standard volumetric or mass units. A great benefit of the thermal mass flow technology is that there is a negligible or very low pressure drop in the pipe. There are no moving parts to interrupt flow and there is no need for additional pressure or temperature compensation to calculate the mass flow rate of the gas.
Other Benefits of Thermal Mass Flow Measurement
There are many benefits of thermal gas mass flow meters over other flow measurement technologies:
- Direct mass flow measurement of air and gases in standard volumetric units (e.g., SCFM or NM3/H) or mass units (e.g., LBS/M or KG/H)
- No additional pressure or temperature compensation required
- Repeatability and exceptionally broad measurement range: up to 1000:1 (100:1 typical)
- Standard linear 4-20mA output proportional to mass flow rate
- No moving parts
- Cost-effective
- Insertion, Inline, and remote* styles
- Measures flow rate and temperature
The Fox Thermal Digital Difference
Fox Thermal is revolutionizing thermal mass flow measurement technology with a series of innovations:
- Microprocessor-based, field-rangeable electronics
- DDC-Sensor™ proprietary flow sensor design*
- Gas-SelectX® field selectable gases / gas mixes without affecting accuracy*
- CAL-V™ and Zero CAL-CHECK® Calibration Validation*
- Free FT View™ Software to configure meter, print calibration validation certificates, run simulations, and more!*
- Data Logger with 7-year history*
*features vary by model number